What is blockchain?
In the recent time, the blockchain technology has become increasingly popular on the Internet. Unfortunately, not so many people understand what is it.
Blockchain is a child of a genius, known under the pseudonym of Satoshi Nakamoto. In the 2008’s publication, he defined his invention as a «peer-to-peer electronic cash system». He wanted to make bitcoin work like cash, so the system should have been able to transfer digital coins correctly (not to send them to the wrong wallet) and prevent double spending. To embody Nakamoto’s dream of the centralized payment system, these goals had to be achieved without the intervention of third parties like banks.
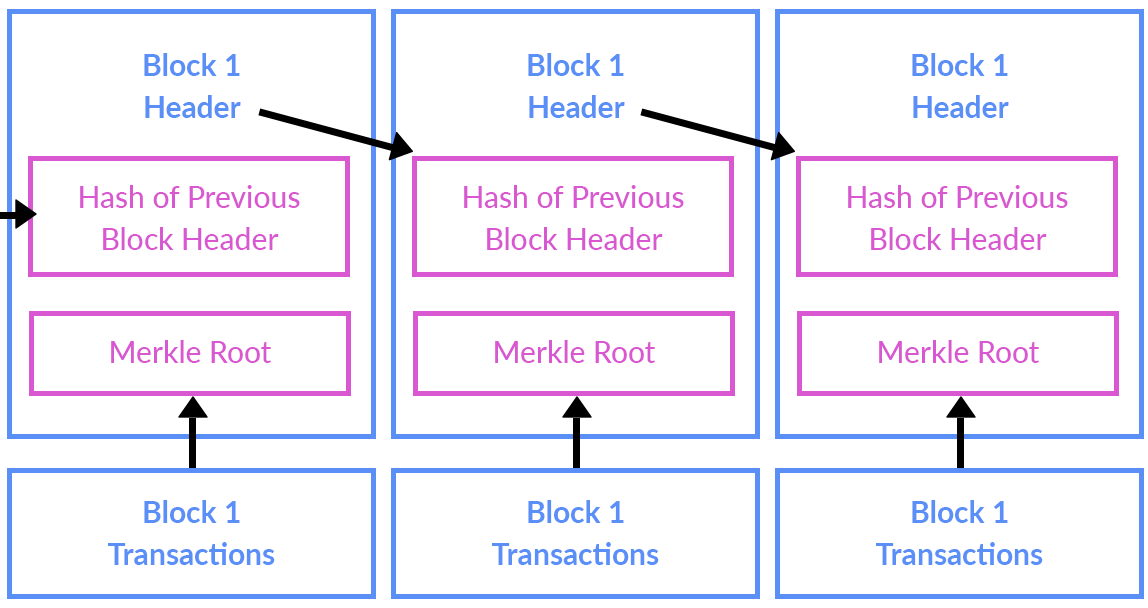
But what is it used for? Originally, a blockchain is a distributed database that is utilized to maintain a continuously growing list of records, called blocks. Each block contains a timestamp and a link to a previous block. A blockchain is typically managed by a peer-to-peer network collectively adhering to a protocol for validating new blocks. By design, blockchains are inherently resistant to data modification. Once recorded, data in any given block cannot be altered retroactively without the alteration of all subsequent blocks and the overall collusion of the network. Functionally, a blockchain can serve as “an open, distributed ledger that can record transactions between two parties efficiently, verifiably and permanently. The ledger itself can also be programmed to trigger transactions automatically.” – Wikipedia says.
Also, it can be called a linked list or a puzzle. Each puzzle is attached to another one by validating the hash of the previous block.
A blockchain can store data on bank and legal transactions, on contracts, voting, etc. Its main difference from regular databases is the decentralization. The chain (registry) is stored on hundreds of thousands of computers which any user has access to. Such system is harder to crack, to spoil or lose the data in it if any hardware or software failure occurs with the server on which the database is stored. This technology is fundamental to the Bitcoin payment network. It guarantees the safety of information on financial transactions between network participants.
What is good about blockchain?
A blockchain can be perceived as kind of a supercomputer that combines a number of nodes that your data is stored securely on. The most valuable thing is that it is impossible to lose such data because it is preserved forever. Data in a blockchain is not only in its final state, but in all the previous ones.
It is almost impossible for hackers to crack this repository because each subsequent block is linked to the previous one. The chain works on numerous computers. That way, hacking a blockchain is almost an attempt to deceive the global computer network, which is unlikely given the current technology development state.
For the majority of network users, the term “blockchain” uniquely associated with Bitcoin. These two concepts are far from being the same, although they are closely linked – a blockchain technology was developed to support Bitcoin. Nobody can control its turnover, and opening a bitcoin-wallet is much easier than it is for any bank account. Today using this mysterious money you can buy everything you want on the Internet. Users of the network highly appreciate the anonymity and transparency of this cryptocurrency. In addition to Bitcoin, there are other examples of the block-based cryptocurrencies, for example, Ethereum, which is appreciated by the owners of small private blockchains.
The advantages of a blockchain technology make it in demand in such spheres of life as banking operations, medicine, logistics, law or music. Let’s look at musicians as an example. Unfortunately, with the traditional scheme of the music publishing, the bulk of income goes to the labels, and composers only get some crumbs. The use of blockchains in the music business could allow the author of the song to post it for the free listening, while drawing up contracts from people using it for private purposes, for example, in a TV series.
A blockchain technology allows you to get rid of intermediaries in many spheres and perform various P2P operations directly between the two sides. For example, this is beneficial for those who want to hire a specialist as, say, a nanny, a driver or a lawyer, without the help of recruiting agencies. In this case, you won’t have to overpay!
But it’s unlikely that the rapid development of this technology can appeal to large companies that have made their fortunes in mediation. Who are they, these middlemen? There are thousands of them, some of the most famous ones are Uber and Airbnb.
The types of blockchain
There are two main types of the blockchain organization: private and public.
In a private blockchain, the creation of blocks occurs centrally. Only the trusted nodes can add blocks. Anyone from outside who wishes to check, can audit and see the chain changing history. Private blockchains can easily update the functionality, that is, monitor the system from the company side.
In a public blockchain, every user, who has the ability to make transactions, can read everything about it. In this case, transactions will be protected by a verification mechanism. All members of the network, such as ordinary users, developers, etc. can control public blockchains. Harmful changes are prevented by updating the protocols. Consequently, the system creates decentralized applications.
Work experience with a blockchain
So, it has been interesting for our team to try out this innovative technology in business. The main challenge was to implement the technology as simply and quickly as possible.
Task: Create a poll on mobile devices using the blockchain technology.
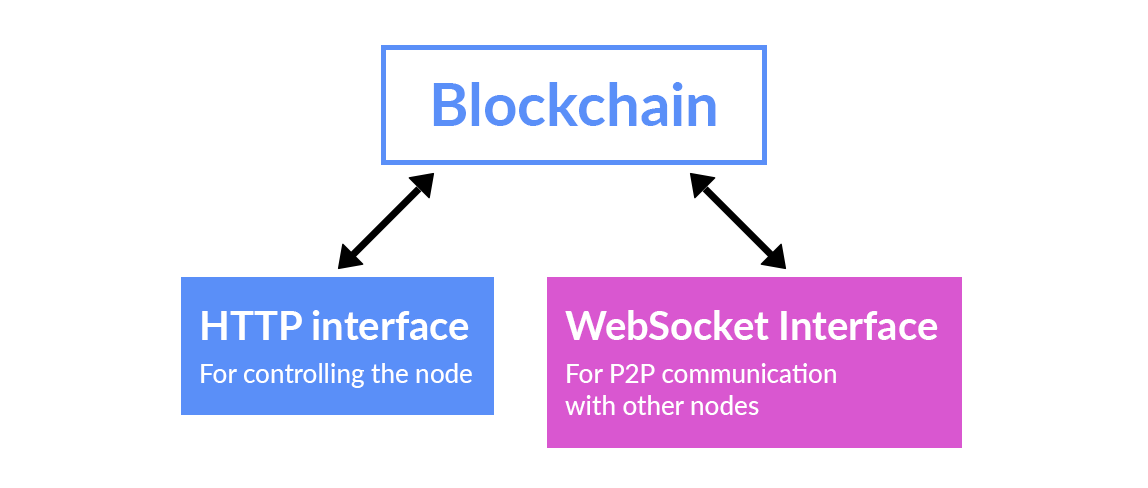
For this task, we have decided to use a private blockchain. Control center was implemented as a backend on Node.js.
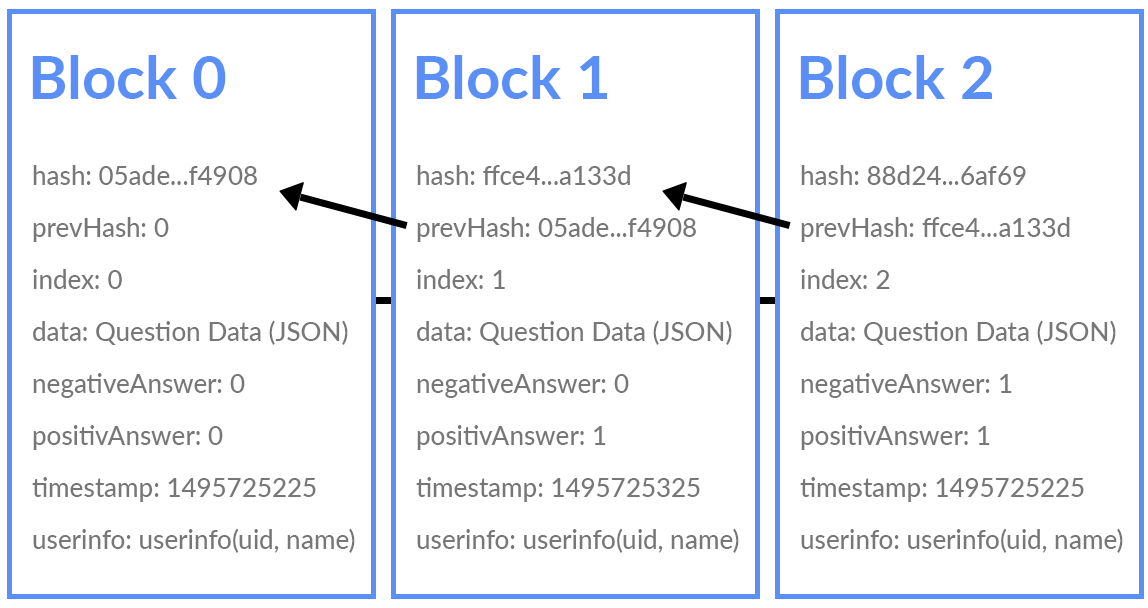
The first logical step is to establish a block structure.
What we need: current hash, a hash of the previous block, block index (number), data that contains the question and answer options, user response, time, user data.
Hash is meant to preserve the chain’s integrity, so every block should be hashed.
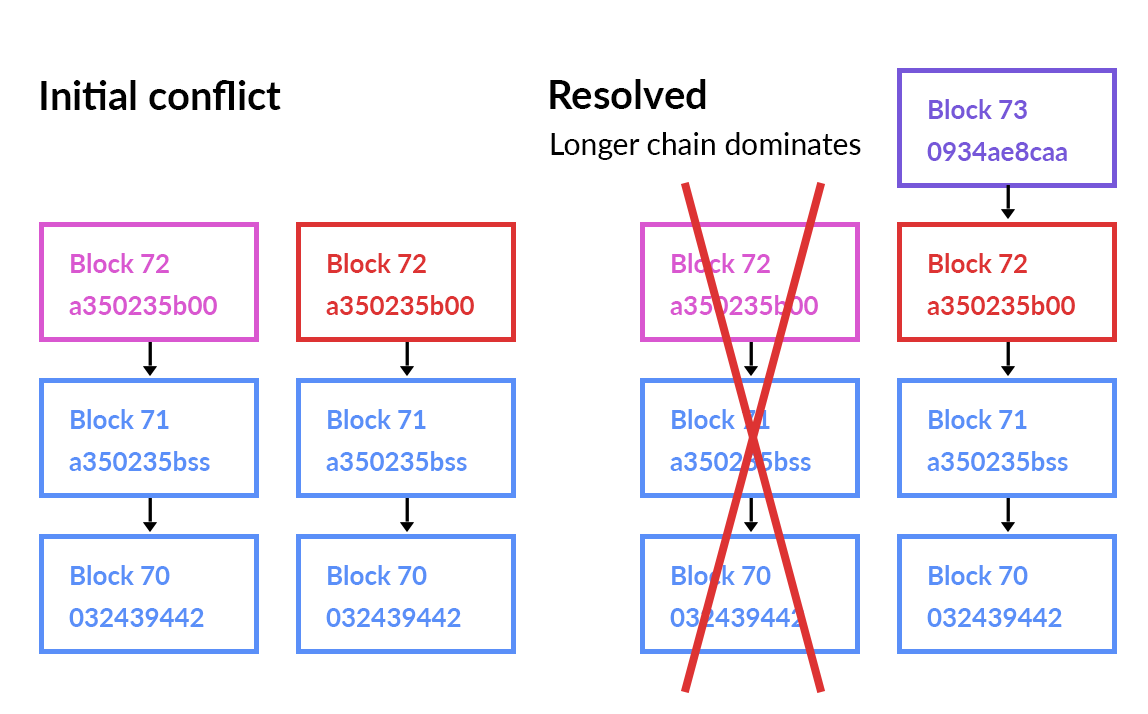
For encryption, we use SHA256. A server stores the chain, which at any time must be validated for integrity. This is necessary when adding a block. We check the integrity of the previous hash, as shown on the scheme. The longest chain has to be selected always in order to prevent any conflicts. If a block passes the validation, it is then added to the chain. Otherwise, an error occurs.
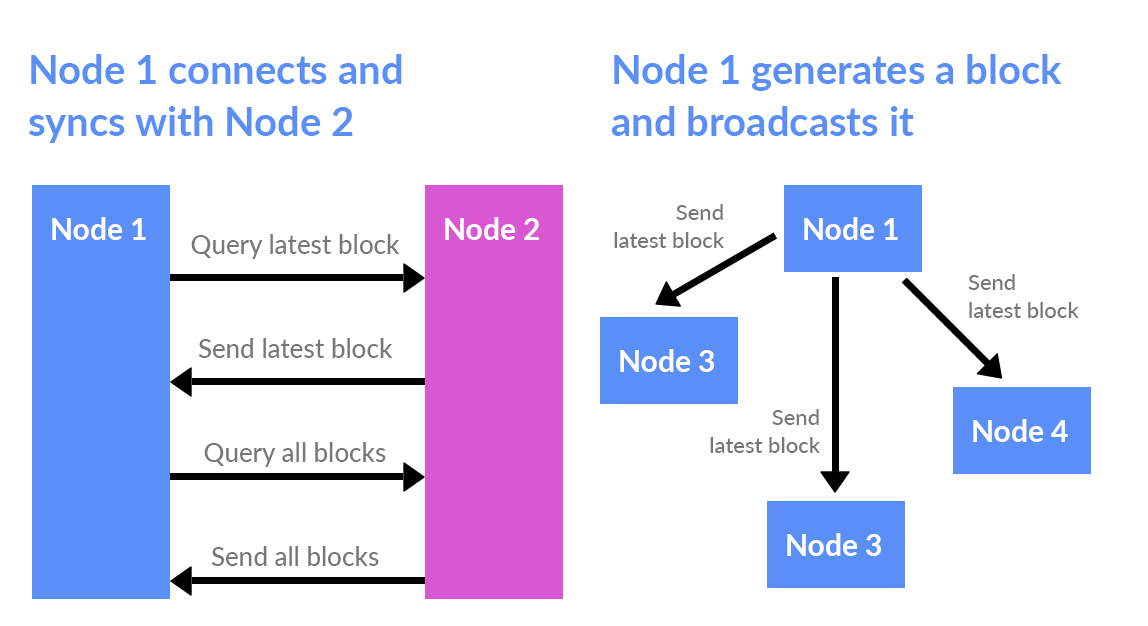
The second important thing to do is to organize the synchronization and broadcasting between all the participants in the voting.
- When a user connects to the network using a web socket, he relies on the last block
- When you create a new block, it is broadcasted to the network
- In a case when a node sees a block, it adds a block to its chain. Or it supports the chain to fill the block, provided that its index is larger than the one of the current block
The server can view the chain, create a new block with a custom response, view the rest of the users.
In such a simple and fast way we implemented voting inside the company, but the question arose that every user could vote the unlimited number of times. The solution to this problem was to assign a unique ID to each user. Help came from Google Firebase which allows making authorization for your application easy. This platform supports social networking authorization. In the result, the chain stores the IDs of the users who have voted, which eliminates repeat votes.
We created a prototype for informational purposes. One of the alleged advantages of a blockchain is the decentralization, but it didn’t seem like a definitive solution, so we decided to test it. True, the advantage of the fact that each participant keeps (or can store) a chain of changes is undeniable, but it can still be outsmarted, and we’ll talk about this later.
Decentralization
In order for the new block to be added to the chain, it has to be validated by checking the previous hash. Validation is carried out according to the protocol. The protocol is created by the author of the contract (the beginning of the chain / first block).
Imagine there are 21 schoolchildren in the classroom (10 girls and 11 boys), and on September 1 they decide to choose the School President using a blockchain. A class teacher creates a contract, in our case, starts a voting for the candidates, and according to the protocol, the new block is considered valid if 51% of the voters give a positive response. Pupils start voting, and at some point, boys decide to falsify the results of the voting in favor of their candidate. By the time of this decision, 8 boys, 6 girls, and the class teacher have voted. The boys understand that they are either losing in the voting or coming out at 50% – 50% at most, by fair means. They decide to alter the chain starting from the second block so that 15 blocks would be substituted for completely different values (advantageous to them). The 7th girl, when she’s giving her voice, will pass the validation of the chain, and in response 8 boys won’t validate her block. And she will have to use a new chain, and the blockchain’s feature is that in a conflict situation, a valid chain is the longest one. Thus the boys will win with their candidate.
For example, Joe wished to become the School President, and the voting took place in the usual way, the whole database was stored on a separate server. Joe asks his brother, the programmer, to help him with that. So his brother hacks the server and changes the outcome. Joe becomes the School President.
If a blockchain was used, then Joe would have to ask the other boys to help him achieve it. And if they declined, Joe would never become the School President.
Conclusion
After using this technology, we have concluded that the blockchain has a lot of pitfalls. As for any system, the rules should be established for all participants. The introduction of the technology requires a large-scale restructuring of a large system with many participants, and each of them should be ready to take risks and bear expenses.
The lack of a legislative framework leads to uncertainty in a variety of issues. In order for the technology to gain trust, it has to meet the standards (public ones, for example). No standards – no correspondence. Despite the decentralization and the absence of any “third parties” attributed to the blockchain, the operation of the system requires the consensus of its participants on many issues. From the very beginning, each blockchain project should develop a system for making decisions which requires the consent of the majority.
About Redwerk
Redwerk is a team of certified experts, who make available high-quality IT outsourcing service for businesses that strive for a robust, stable and impressive product. Redwerk is a customized software development company, that engages masters of their trade with proactive approach to deliver on exactly what customer requires. We do appreciate those who trust us, so be the one!