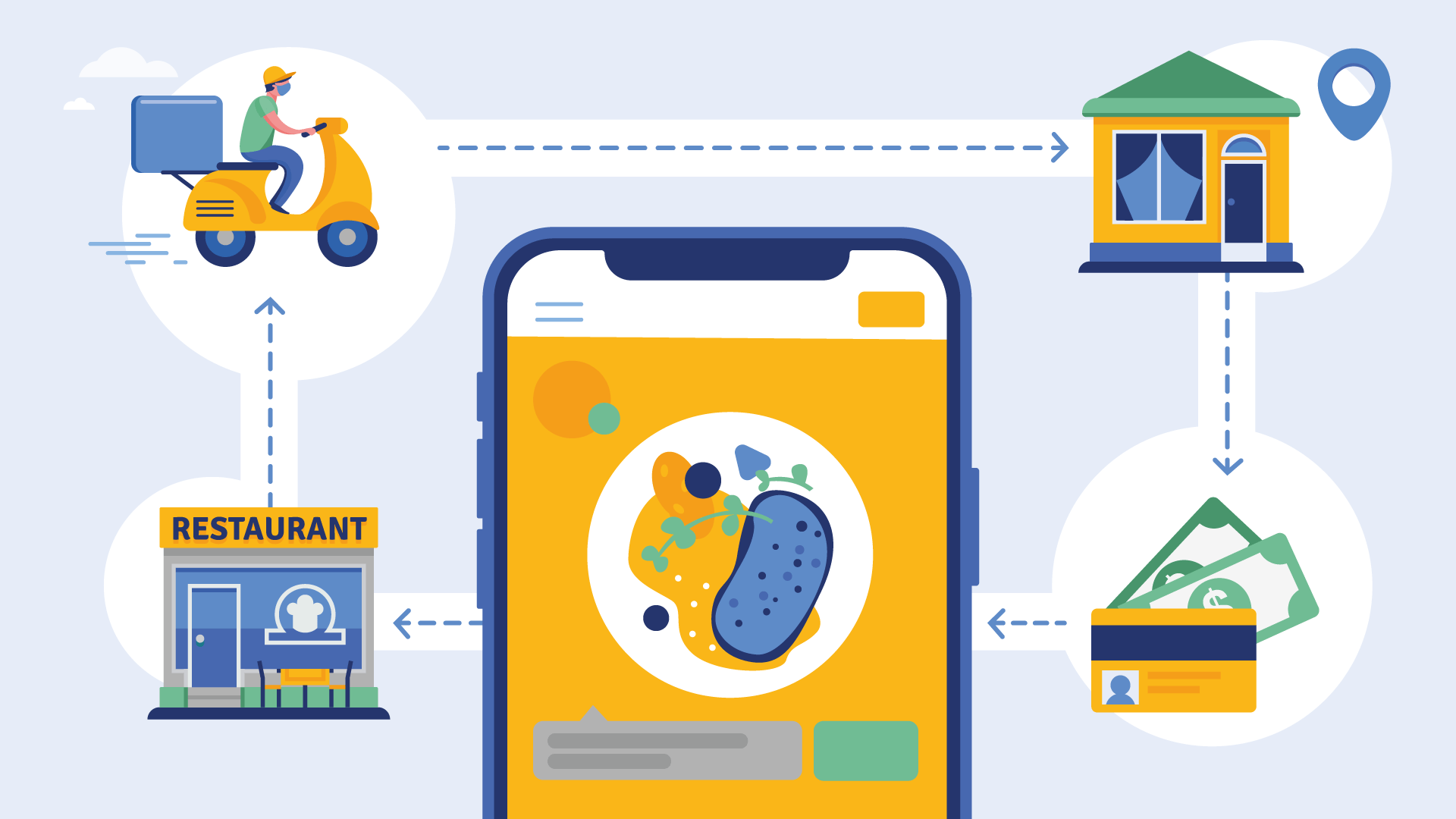
Building a delivery app is a viable and lucrative venture because it brings multiple benefits to consumers, restaurant owners, and entrepreneurs who created those food ordering apps.
Consumers enjoy the convenience and a broad choice of cuisines conveniently grouped in a single solution. Restaurant owners increase the exposure of their brand, increase customer loyalty, and gain a new channel for marketing campaigns. And entrepreneurs earn money by taking commissions from restaurants, charging delivery fees, or implementing other monetization schemes. It’s a win-win for everyone.
Have you ever thought about how to make your own food delivery app? In this article, we’ll cover the essentials of food delivery app development so you know how to kick start and excel in the on-demand meal ordering business. Let’s dive right in!
Why food delivery apps are the future of dining
Food delivery apps are revolutionizing dining, becoming essential as the COVID-19 pandemic underscored their necessity. With life remaining busy, the demand for these services continues, with user numbers expected to reach 4.5 million by 2027.
The online food delivery market is set to exceed $1.4 trillion by 2027, reflecting the rise of delivery-only kitchens. Major fast-food chains have launched their apps to enhance customer loyalty through personalized experiences.
For traditional dine-in spots, an online platform is key to controlling customer data. Meanwhile, smaller venues might find opportunities in third-party solutions that offer competitive advantages over giants like DoorDash.
In summary, food apps offer numerous benefits: they streamline customer service, widen market reach, reduce overhead costs, create new marketing avenues, improve operational efficiency, and enhance customer loyalty through effective reward programs.
How to make a food delivery app: the business side
Drawing on our decades-long expertise in SaaS and mobile app development as well as extensive market research, we curated a step-by-step guide on how to start food ordering app development. Let’s first go over the business side of things.
Conduct market research
Conducting detailed market research is vital. Despite strong competition and the presence of dominant online food delivery services, identifying niche opportunities in local markets can uncover unmet needs. For example, the exit of UberEats from Ukraine or Glovo from the Middle East highlights gaps that can be exploited.
Think of what you can do better than competitors: offer a wider variety of healthy options, comprehensive vegan menus, and traditional dishes. Additionally, cater to special dietary needs and explore selling groceries alongside prepared meals.
For ventures that successfully capture a significant customer base, exploring mergers or acquisitions can be a strategic move to expand resources or secure profits, as seen in the mergers of Seamless and GrubHub in 2013, Maple and Deliveroo in 2017, and DoorDash’s acquisition of Caviar in 2019.
Choose a business model
After detailed market research, the next step involves selecting a suitable business model. Most startups revert to traditional frameworks: either the aggregator approach or the full cycle delivery system.
The Aggregator Scheme
This approach positions itself as a mediator, combining meal options from multiple restaurants into one application. Its popularity arises from solving common issues such as non-optimized restaurant websites. Restaurants receive extra visibility and a chance to boost sales, with the flexibility to use their delivery team or the aggregator’s services. Domino’s partnership with Uber Eats, maintaining their delivery operations, illustrates this model. Zomato and Deliveroo offer restaurants the choice to fulfill orders with their drivers.
Monetization: 10-30% commission per order, paid listings.
The Full Cycle Delivery Scheme
This model suits smaller establishments lacking resources for their delivery operations, covering marketing, order handling, and delivery. Delivery companies may charge up to 30% commission for these all-encompassing services.
Monetization: 10-30% commission per order plus delivery fees, paid listings.
Direct Delivery
This model benefits restaurants aiming for control over customer data and experiences while avoiding high aggregator fees. It requires a significant initial investment but leads to autonomy over the long term. Restaurants take on the development and maintenance of the application, meal preparation, and delivery operations.
Monetization: Delivery fees, potentially higher meal prices for consumers.
The choice of model directly impacts the development scope of a food delivery app:
- Three applications for the aggregator model (customer, restaurant, CRM).
- Four applications for the full cycle and direct delivery models, adding a courier application.
Remember that a smooth user experience relies on seamless collaboration across all platforms, supported by an intricate system of app integrations. Customers perceive only the surface of a complex operational structure designed to facilitate efficient food delivery.
Find a food delivery app development company
Developing a food delivery app involves UI/UX design, development, API integration, and testing. It’s advisable to hire experts. Look for a company with experience in delivery apps, offering managed services to alleviate management tasks.
Redwerk has completed over 250 projects globally. For Quandoo in Germany, we created an iOS app for restaurant management now used by 18,000 restaurants in 12 countries. We also developed Borjomi Restoguide, featuring a user-friendly interface, restaurant search, favorites, reviews, and analytics.
We provide business analysis for complex projects to ensure clear requirements, reducing the need for costly changes.
Design a minimum viable product
With a business model in place, entrepreneurs can focus on refining their plans, often constrained by resources. This situation leads to considering a minimum viable product (MVP) to test basic functionalities without extensive initial investment, allowing for adjustments based on user feedback.
Customer App
The customer app enables users to explore restaurant menus and place orders online. Prioritizing UI/UX design is crucial for a seamless experience. Analyzing top food delivery apps helps identify what works and what doesn’t, from location permissions to intuitive navigation and signup options.
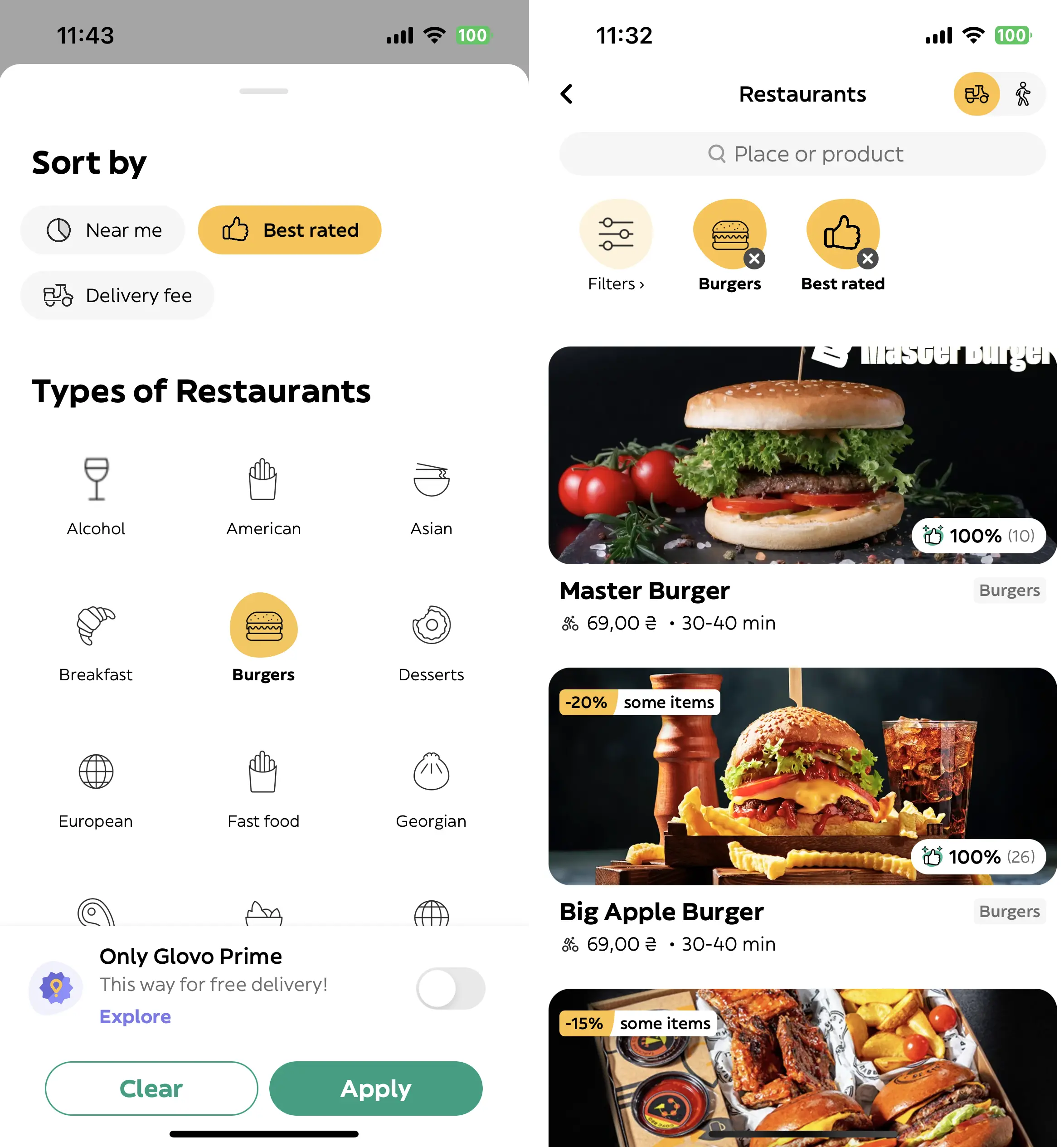
Key features of a customer app:
- Splash Screen: Captures attention with animations and branding
- Registration/Login: Authenticates users and secures access
- Profile Page: Organizes user details, order history
- Search Bar: Eases meal meny and restaurant discovery
- Order Placement: Enables ordering meals
- Payment Options: Enables effortless payment online
- Order Tracking: Provides real-time delivery updates
- Customer Support: Facilitates issue resolution
A well-designed customer app is vital, but its effectiveness depends on seamless integration with a corresponding restaurant app.
Restaurant app
A restaurant app is a solution for employees of the restaurant. It is synced with the customer and courier apps and allows restaurant administrators to manage every single order effectively and keep everyone on the same page.
Key features of a restaurant app:
- Registration/Login: Authenticates restaurant personnel
- Menu Management: Allows restaurants to add, remove, and put on hold meals
- Notifications: Alerts for new orders or courier arrivals
- Order Handling: Supports order acceptance, preparation, and delivery tracking
- Customer Communication: Addresses order questions or issues
- Payments: Manages transactions
- Sales Analytics: Evaluates performance
- Support: Maintains clear communication
Courier app
Designed for delivery personnel, this app functions like Uber for drivers but focuses on food delivery. It enhances efficiency by streamlining order pickups, routing, and customer interactions.
Key features of a courier app:
- Registration/Login: Provide access to order assignments
- Order Reception: Manages availability for pickups
- Navigation: Guides couriers from pickup to delivery
- Notifications: Offers reminders and tips
- Communication: Facilitates contact with restaurants or customers
- Delivery Log: Tracks completed deliveries
- Earnings Overview: Displays income
- Cashout: Simplifies payment withdrawals
- Support: Provides comprehensive guidance for couriers
CRM System
A CRM is vital for managing relationships between all stakeholders to ensure optimal service delivery. It supports customer service teams in overseeing the customer journey and addressing issues as needed.
Basic requirements for a CRM system:
- Customer Profiles: Holds contact and personal information
- Lead/Deal Tracking: Identifies profitable partnerships and opportunities
- Invoice Management: Ensures accurate billing and accounting
- Customer Support: Directs significant concerns for resolution
Integrating a third-party CRM can expedite setup, though testing multiple systems to find the best fit is necessary for aligning with specific business challenges and workflows.
How to make a food delivery app: the tech side
After finalizing the app’s features, the next step is choosing the tech stack. There’s no one-size-fits-all solution, so the focus should be on enabling developers to efficiently manage and update the app’s codebase.
The selection of a tech stack depends on your budget, user demographics, scalability, and planned integrations. Here’s an overview of the technical considerations for a delivery app’s architecture.
System design
The system design forms the technical backbone of the food delivery app, where business owners decide on implementing their business strategies through technology. Opt for a scalable architecture that minimizes maintenance needs. Choosing durable, future-proof technologies saves costs on long-term overhauls. Key elements include programming languages, development platforms, frameworks, and databases, all critical for crafting the system’s foundation.
Payment gateway integration
Smooth financial transactions that do not frustrate consumers are what most companies need from a payment system. When deciding on a payment integration, keep in mind that users trust big, well-established brands. One more thing to consider is the business location as there may be local payment providers that people are familiar with, which in turn makes them trustworthy in their eyes. Some of the most well-known and secure payment companies are OneSignal, Firebase, Leanplum, AWS.
Mapping and tracking services
Can you imagine a food delivery app without the option to track the order location? Or a newly hired driver using a physical map or an extra phone simply for navigation purposes? Ridiculous, right? Having a visually appealing and easy-to-read map is what most delivery companies aspire to, and this goal seems a piece of cake if they can afford Google Maps API. The latter is an absolute leader in the market; however, alternatives do exist: TomTom, OneLayers, MapBox, HERE, and many others.
Analytics software integration
Making data-driven decisions is one of the factors that set prosperous and stagnant businesses apart.. An effective marketing campaign is impossible without studying user behavior. Fortunately, there are plenty of tools for gathering user data and compiling it into distinguishable chunks of information. The choice of software depends on the type of data that needs to be analyzed. Some options to consider are as follows: Google Analytics, Power BI, Oracle, Tableau.
Deployment options
As business owners approach launch, deciding on a deployment option becomes crucial. The choices boil down to setting up an in-house server or opting for cloud services. For start-ups and medium-sized businesses, cloud servers are often the better choice, despite potential drawbacks like compatibility issues and security concerns. They offer cost-effective hosting and storage solutions for immediate operation commencement. Leading providers include AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
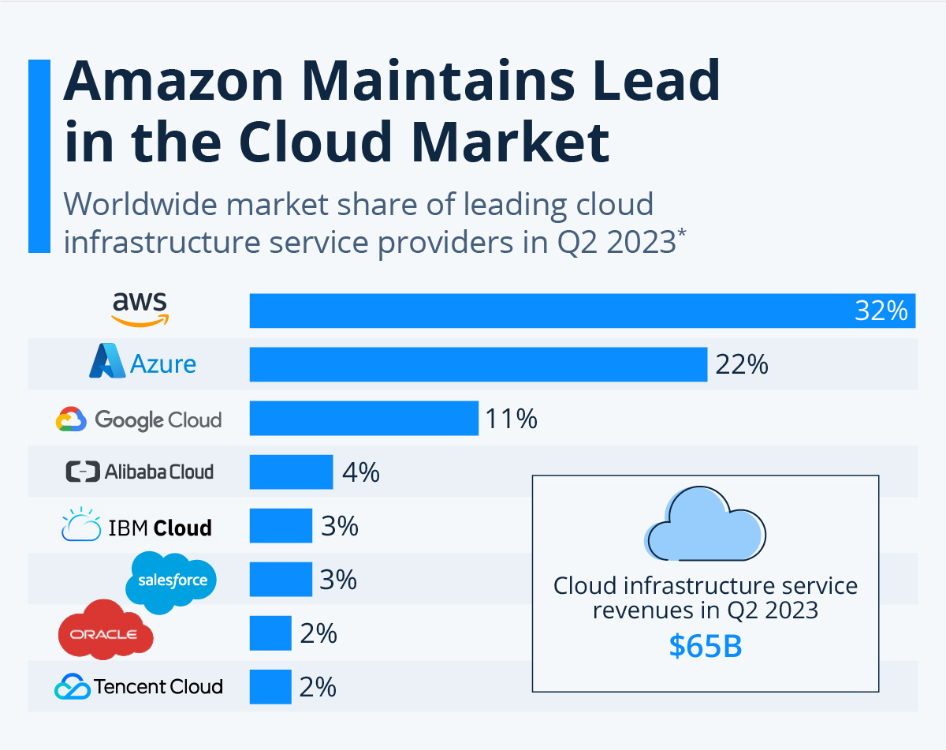
If you have no idea what features to check while choosing a cloud service provider, make sure to read this article, in which we compare AWS against Azure and Google.
Maintenance and Support
Post-launch, attention turns to maintenance and support. Even well-crafted products may encounter unforeseen issues, such as handling spikes in user traffic or maintaining consistent app performance. To address potential challenges and ensure long-term functionality, investing in a dedicated development team for ongoing support is a wise strategy.
How much does it cost to build a food delivery app?
Now that you know how to start a food delivery service app and what it entails, you probably wonder how much it costs and how fast you’ll receive your MVP. Here, we discuss in detail the factors affecting the app development timeline.
As for the pricing, it varies based on the number and complexity of features and the vendor you hire. Software development services are often outsourced to Eastern European countries, such as Ukraine, Poland, or Romania, to achieve the best quality-to-cost ratio.
At Redwerk, we use the Time & Material model to estimate the time and cost of building an app. Considering all the projects we have completed, we know how much time we usually need to develop a common feature. For example, a splash screen may require only one hour, whereas a login screen requires ten or more.
Food delivery app rough estimation, man-hours
The total cost for launching a food delivery project depends on the number of supplementary apps one needs, monthly fees for integrations and cloud server services, quality assurance, software maintenance, and overall support of the entire business infrastructure.
Summing up
Developing a food delivery app is a long and time-consuming journey; however, it may still be a viable idea if a local market is not oversaturated with similar businesses. With the help of a professional business analyst and a dedicated team, any business venture is possible!
Achieve your goals together with Redwerk!
How much does it cost to build a food delivery app?
See the estimate for one of our projects with feature breakdown, hourly rates, and total cost.